
[ad_1]
Excerpts from a study initially published in the International Journal of Dream Research – modified by addition of pictures – Stumbrys, T., & Erlacher, D. (2012). Lucid dreaming during NREM sleep: two case reports. International Journal of Dream Research, 5(2), 151–155. https://doi.org/10.11588/ijodr.2012.2.9483
“Lucid Dreaming During NREM Sleep: Two Case Reports
Tadas Stumbrys1 & Daniel Erlacher2
1 Heidelberg University, Germany 2 University of Bern, Switzerland

,REM dreams reports are typically longermore bizarremore perceptually alivemore emotionally charged and more motorically animated,
Whereas NREM dream reports contain more thought-like mentoring and representation of current concerns,


…Yet one lucid dream induction study (Dane, 1984), which used post-hypnotic suggestion as a means to induce lucidity, found an unusually high number of NREM lucid dreams,
REM sleep and NREM sleep seem to have different brain activation patterns (Hobson et al., 2000). During NREM sleep the brain is generally less active than during both REM sleep and wakefulness, while the overall activation during REM sleep is similar to wakefulness…
Cortical areaswhich are selectively deactivated during R.E.M. sleep and the activation of which is associated with lucid dreamingsuch as the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, precuneus, cuneus…are also deactivated during NREM sleep,
…Purcell and her colleagues (1986), who found that overall self-reflectiveness in NREM dreams is lower than self-reflectiveness in REM dreams…
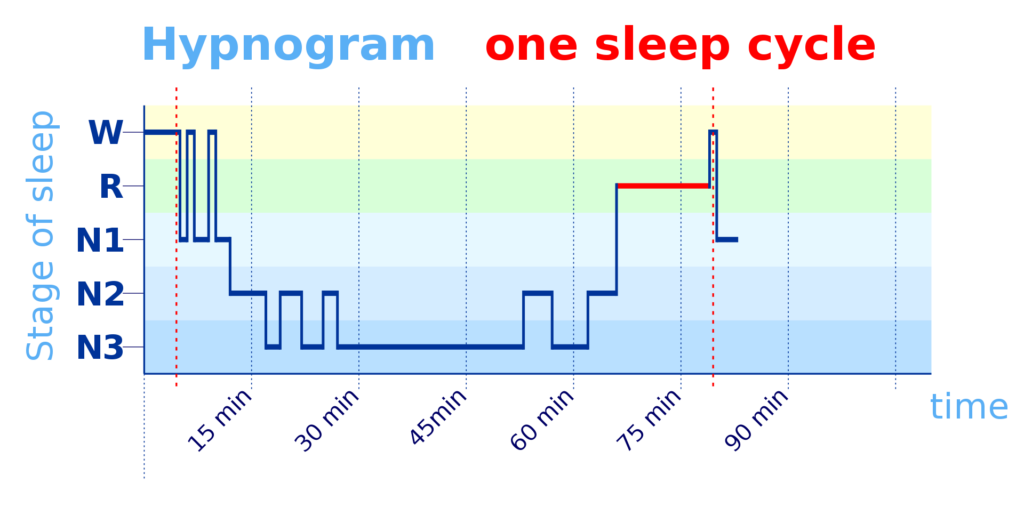
…Findings from the earlier studies…suggest that of all NREM sleep stages lucid dreaming can most often occur during N1however such lucid dreams are usually quite short…In fact, dreams collected from N1 and REM sleep seem to be strikingly similar.…as well as brain EEG activity during both these stages…
,Wake-Initiated Lucid Dreaming (WILD)where the dreamer aims to enter the dream directly from wakefulness by retaining consciousness while falling asleep …and some of these techniques are based on concentration on hypnagogic imagery occurring during N1 sleep,
N2. Lucidity during N2 also seems to be possible.… yet less frequent and usually preceded by some arousal (which might help to initiate lucidity). Lucid dreams are also brief.
N3. Up to our knowledge no lucid dream reports so far had been obtained from N3 (deep sleep) stages. ,

…Another interesting observation is that all possible instances of NREM lucidity have been observed so far were only from female participants… Although it is premature to assert any gender differences in relation to NREM dream lucidity, this is something that could be taken into account in future studies.
future studies should also clarify whether brain regions involved in attaining lucidity in REM sleepnamely prefrontal, occipito-temporal cortices, precuneus, cuneus, parietal lobules…are also the ones involved in attaining lucidity in NREM sleep,

,NREM dream reports are usually less vivid with lesser involvement and are more thought-like (Hobson et al., 2000). This parallels a distinction made in Tibetan sleep and dream yoga,

While dream yoga aims to develop awareness in dreamsthe aim of sleep yogawhich is considered to be more difficult to master, is to develop awareness in dreamless sleepwhere no dream images is present. Therefore it might be possible to speculate that a Parallel could be made between dream yoga and attaining dream lucidity in REM sleep, and sleep yoga and attaining dream lucidity…in NREM sleep…,
How does this relate to WILD?
What are the neurological differences between WILD and DILD?
How do neurological and sleep phase differences make WILD and DILD differ from each other in regards to consistency, lengths, and overall experience?
[ad_2]